Heart Rate Variability – What is it? Should I listen to it?
HRV has gained popularity as a training tool, especially in the realm of endurance sports and general fitness, so what is it and how can it benefit you? Heart rate variability (HRV) is a measure of the variation in time between successive heartbeats. It’s often used as a tool to assess the autonomic nervous system’s activity, which consists of the sympathetic (fight or flight) and parasympathetic (rest and digest) branches.
Here’s an overview of its effectiveness
Training Adaptation and Recovery:
HRV is considered a valuable tool for monitoring the body’s response to training stress and gauging overall recovery. A higher HRV often indicates a more adaptable and recovered state, while a lower HRV might suggest fatigue or insufficient recovery.
Individualized Training Plans:
By tracking HRV regularly, athletes and fitness enthusiasts can potentially tailor their training plans to their individual recovery needs. Adjusting training intensity or incorporating rest days based on HRV trends may help prevent overtraining and optimize performance.
Stress Management:
HRV can be influenced by factors beyond exercise, including stress, sleep, and lifestyle. Monitoring HRV can provide insights into the overall stress load on the body, helping individuals manage their training load in the context of daily life stressors.
Preventing Overtraining:
HRV monitoring is often used as a preventive measure against overtraining, which can lead to decreased performance, increased risk of injury, and various health issues. Catching signs of overtraining early allows for adjustments in training volume and intensity.
Readiness to Train:
Some athletes use HRV to assess their readiness to tackle a particular training session on a given day. A lower HRV might suggest that the body needs more recovery before engaging in a high-intensity workout.
Sleep Quality Assessment:
Sleep quality is a crucial factor in recovery. Changes in HRV patterns can indicate disruptions in sleep, providing insights into the impact of sleep on overall recovery.
Biofeedback Training:
Biofeedback tools, including HRV, can be used in biofeedback training to help individuals learn how to regulate their physiological responses to stress. This can contribute to improved performance and stress management.
It’s important to note that while HRV can be a valuable tool, it’s not a standalone metric, and its interpretation should consider individual variations and other contextual factors. Additionally, the accuracy and reliability of HRV measurements depend on the quality of the monitoring device and consistent measurement protocols.
How do I use this to manage my training?
Using heart rate variability (HRV) to manage training load involves monitoring your HRV over time and adjusting your training intensity and volume based on the insights gained. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to incorporate HRV into your training load management:
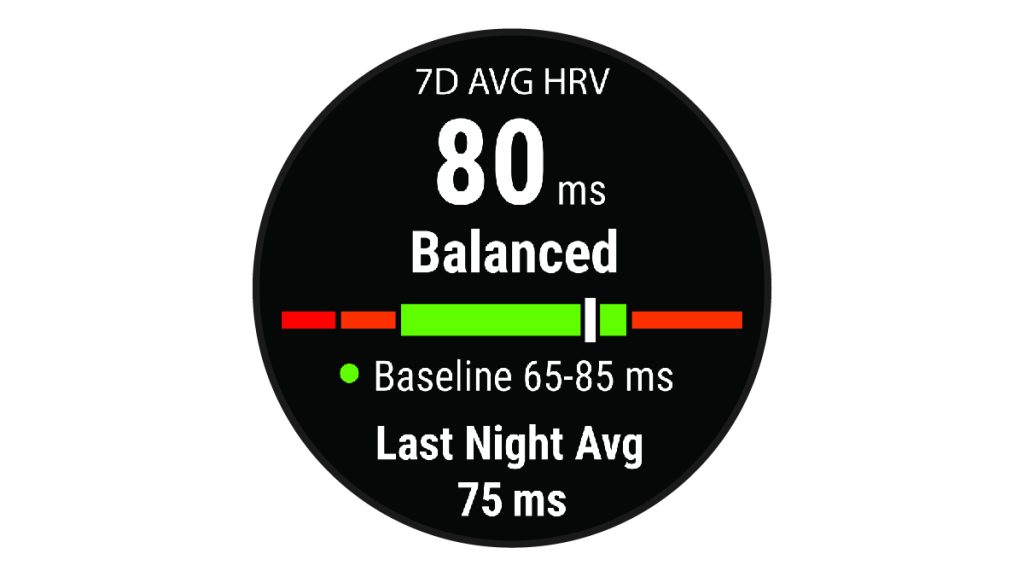
Establish a Baseline:
Before using HRV for training load management, establish a baseline by monitoring your HRV consistently over a few weeks in a stable training period. This baseline will help you understand your typical HRV values when adequately recovered.
Choose a Monitoring Device:
Select a reliable HRV monitoring device. This can be a chest strap, a wearable fitness tracker, or a smartphone app that measures HRV. Ensure that the device and app you choose are suitable for your needs and provide accurate measurements.
Consistent Measurement Protocol:
Measure your HRV at the same time each morning under similar conditions (e.g., before getting out of bed). Consistency in measurement conditions is crucial for accurate and meaningful data.
Track Trends:
Monitor trends in your HRV over time. Fluctuations in HRV can be normal, but significant deviations from your baseline may indicate changes in your recovery status.
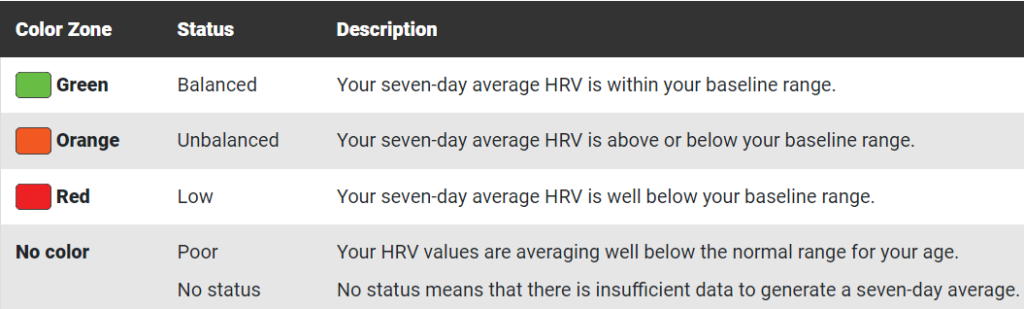
Establish Your Personal Zones:
Define individual HRV zones based on your baseline. These zones can include a green zone (well-recovered), yellow zone (moderate recovery), and red zone (poor recovery). These zones will guide your training decisions.
Adjust Training Load:
Green Zone: If your HRV indicates good recovery, you can stick to your regular training plan or consider pushing yourself a bit harder.
Yellow Zone: In a moderate recovery state, you may choose to reduce training intensity or volume. Focus on lighter workouts, active recovery, or additional rest days.
Red Zone: When HRV indicates poor recovery, consider taking a complete rest day or engaging in very light activities. Avoid intense or high-volume workouts.
Consider Contextual Factors:
Take into account other factors influencing recovery, such as sleep quality, stress levels, and overall well-being. HRV should be one tool among others in your comprehensive approach to training load management.
Reassess Periodically:
Periodically reassess your baseline and adjust your HRV zones as needed. Changes in fitness levels, lifestyle, or training goals may necessitate updates to your HRV monitoring strategy.
Combine with Subjective Measures:
Consider incorporating subjective measures of well-being, fatigue, and muscle soreness into your overall assessment. Combining objective HRV data with subjective feedback can provide a more comprehensive picture of your recovery status.
Remember that while HRV is a valuable tool, it’s just one aspect of a holistic approach to training load management. Individual responses to training can vary, so use HRV data in conjunction with other information to make informed decisions about your training plan.
If you need any help with your training our coaches are here to help!